Ethernet

What is Ethernet?
Ethernet is the most common wired networking technology used in homes, offices, and data centers. It allows computers and other devices to communicate over a local area network (LAN) using cables and standardized protocols.
Ethernet Cable Wiring Standards
Ethernet cables use twisted pairs of wires to carry data. They use an RJ-45 connectors and there are two main wiring schemes used to arrange the wires in those connectors:
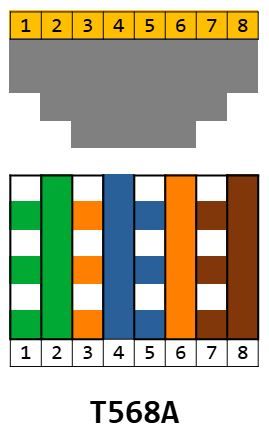
T568A
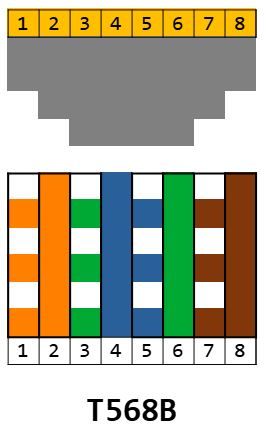
T568B
T568B is more commonly used in commercial networks, while T568A is often used in residential installations.
Cable Types
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair)
UTP cables have no shielding around the pairs of wires. They are lightweight, affordable, and widely used — but more prone to electromagnetic interference.
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair)
STP cables have extra shielding to protect the signal from interference. These are used in environments with lots of electrical noise.
F/STP (Foiled Shielded Twisted Pair)
This type of cable includes foil around each twisted pair and braided shielding around the entire cable for maximum protection.
Cable Types by Purpose
Straight Through Cable
Used to connect different types of devices, like:
- Computer → Switch
- Router → Switch
Both ends follow the same wiring scheme (typically T568B - T568B).
Crossover Cable
Used to connect same-type devices, like:
- Computer → Computer
- Switch → Switch
One end uses T568A, and the other uses T568B.
Ethernet Cable Categories
Each cable category supports different speeds, frequencies, and maximum distances.
| Category | Max Speed | Max Bandwidth | Max Distance @ Max Speed | Min Cable Type Needed | Shielding | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat 1 | N/A (voice only) | - | - | N/A | None | Used in old telephone lines |
| Cat 2 | 4 Mbps | ~1 MHz | 100 m | Token Ring networks | None | Obsolete |
| Cat 3 | 10 Mbps | 16 MHz | 100 m | 10BASE-T | None | Also used in early telephone systems |
| Cat 4 | 16 Mbps | 20 MHz | 100 m | Token Ring LAN | None | Obsolete |
| Cat 5 | 100 Mbps | 100 MHz | 100 m | 100BASE-TX | None | Now replaced by Cat 5e |
| Cat 5e | 1 Gbps | 100 MHz | 100 m | Gigabit Ethernet | Optional | Enhanced Cat 5; very common |
| Cat 6 | 1 Gbps (10 Gbps up to 55 m) | 250 MHz | 100 m (1G), 55 m (10G) | 10GBASE-T | Optional | Tighter specs than Cat 5e |
| Cat 6a | 10 Gbps | 500 MHz | 100 m | 10GBASE-T | Usually shielded | Suitable for data centers |
| Cat 7 | 10 Gbps | 600 MHz | 100 m | 10GBASE-T | Always shielded | Not officially recognized by ANSI/TIA |
| Cat 8 | 25–40 Gbps | 2000 MHz | 30 m | 25G/40GBASE-T | Fully shielded | Data center/high-performance use only |
Ethernet Naming Conventions (BASE Standards)
In Ethernet, names like 10BASE-T or 1000BASE-SX follow this format:
[Speed][BASE][Signaling Type]
- Speed: Data rate in megabits or gigabits per second
- BASE: Short for "baseband" (Ethernet always uses baseband signaling)
- T / F / SX / LX / LR / SR / ER / BX / CX / CR / SR4 / LR4: Indicates the physical medium and signaling type:
- T = Twisted pair (copper)
- F = Fiber (general)
- SX = Short wavelength over multimode fiber
- LX = Long wavelength over singlemode or multimode fiber
- LR = Long Reach over singlemode fiber (~10 km)
- SR = Short Reach over multimode fiber (~100–300 m)
- ER = Extended Reach over singlemode fiber (~40 km)
- BX = Bidirectional over a single strand of fiber (uses different wavelengths for TX/RX)
- CX = Copper (typically very short-range DAC)
- CR = Copper Twinax (used with SFP+/QSFP+ for short links)
- SR4 = 4-lane Short Reach (parallel fiber, e.g., 40G/100G)
- LR4 = 4-lane Long Reach (parallel fiber over long distances)
Ethernet BASE Standards (Grouped by Medium)
Copper-Based Ethernet Standards (Twisted Pair)
| Standard | Speed | Cable Type | Max Distance | Connector | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10BASE-T | 10 Mbps | Cat 3 | 100 m | RJ-45 | Classic Ethernet over copper |
| 100BASE-TX | 100 Mbps | Cat 5 | 100 m | RJ-45 | Fast Ethernet |
| 1000BASE-T | 1 Gbps | Cat 5e | 100 m | RJ-45 | Gigabit Ethernet |
| 2.5GBASE-T | 2.5 Gbps | Cat 5e | 100 m | RJ-45 | Intermediate speed, backward compatible |
| 5GBASE-T | 5 Gbps | Cat 6 | 100 m | RJ-45 | Midway upgrade without needing Cat 6a |
| 10GBASE-T | 10 Gbps | Cat 6a | 100 m | RJ-45 | 10G Ethernet over copper |
| 25GBASE-T | 25 Gbps | Cat 8 | 30 m | RJ-45 | Data center optimized high-speed copper |
| 40GBASE-T | 40 Gbps | Cat 8 | 30 m | RJ-45 | Maximum-speed Ethernet over twisted pair copper |
Fiber Optic Ethernet Standards
| Standard | Speed | Fiber Type | Max Distance | Connector | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100BASE-FX | 100 Mbps | Multimode | 2 km | SC/ST | Fast Ethernet over fiber |
| 1000BASE-SX | 1 Gbps | Multimode | 220–550 m | LC/SC | Short wavelength, used in LANs |
| 1000BASE-LX | 1 Gbps | Singlemode/Multimode | 5–10 km | LC/SC | Long wavelength laser, long distance support |
| 10GBASE-SR | 10 Gbps | Multimode | ~300 m | LC | Short range 10G, typical for data centers |
| 10GBASE-LR | 10 Gbps | Singlemode | 10 km | LC | Long range over singlemode fiber |
| 40GBASE-SR4 | 40 Gbps | Multimode (parallel) | ~100 m | MPO | Parallel fiber, short high-speed connections |
| 100GBASE-SR4 | 100 Gbps | Multimode (parallel) | ~100 m | MPO | Core switching, aggregation in modern networks |
Coaxial Ethernet Standards (Legacy)
| Standard | Speed | Cable Type | Max Distance | Connector | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10BASE-2 | 10 Mbps | Thin coaxial | 185 m | BNC | "Cheapernet", used in small networks |
| 10BASE-5 | 10 Mbps | Thick coaxial | 500 m | AUI | First-generation Ethernet (obsolete) |
Key Notes
- T → Twisted pair copper (Cat 5, 6, 8, etc.)
- SX/LX/LR/ER → Fiber optic (short, long, extended reach)
- BASE → BASE stands for baseband transmission (vs broadband). Always means baseband signaling (one signal at a time)
- Backward compatibility is common (e.g. 2.5GBASE-T works on Cat 5e)
- RJ-45 connectors dominate copper standards. RJ-45 is the standard connector for most copper (twisted pair) Ethernet standards.
- Fiber standards use SC, LC, or MPO connectors depending on mode and speed.
- Fiber options are ideal for long distances, high EMI environments, or backbone connections.
- Coaxial is obsolete but included for historical context.
Sources:
- https://www.cableorganizer.com/learning-center/articles/t568a-vs-t568b.php
- https://www.truecable.com/blogs/cable-academy/t568a-vs-t568b#
- https://www.practicalnetworking.net/stand-alone/ethernet-wiring/
- https://www.electronics-notes.com/articles/connectivity/ethernet-ieee-802-3/cables-types-pinout-cat-5-5e-6.php